Mixing ratio
Mixing Ratio and Temperature
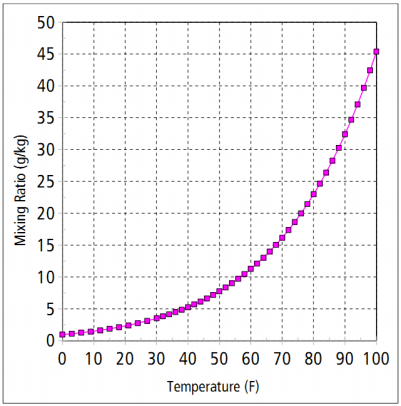
Water vapor capacity of air as a function of temperature. The water vapor unit shown is known
as mixing ratio: the grams of water vapor that can be present in each kilogram of air. For example, air with a temperature of 80 F has a capacity of about 23 g/kg of water vapor.
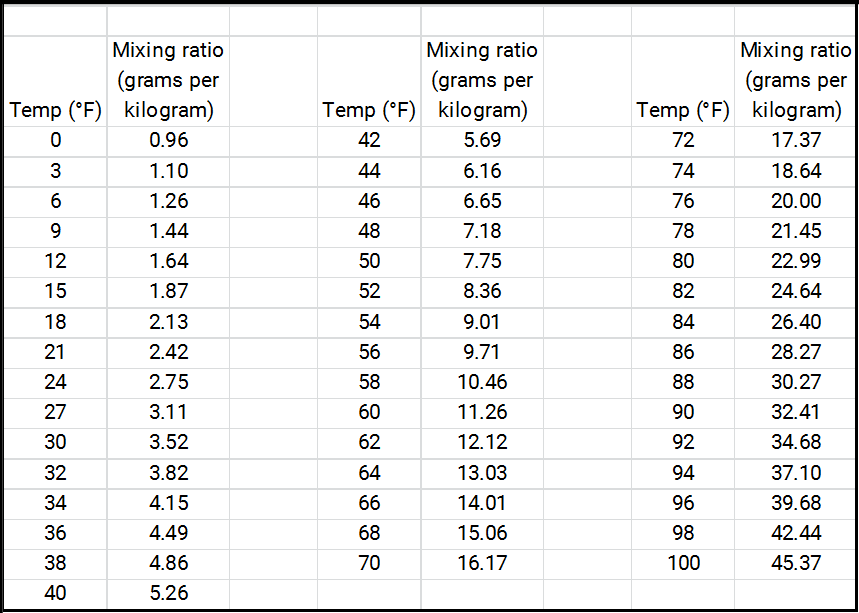
Water vapor capacity of air as a function of temperature, in table form.
Usage Reminders
When you are trying to calculate relative humidity, remember the relationships we've talked about in class:
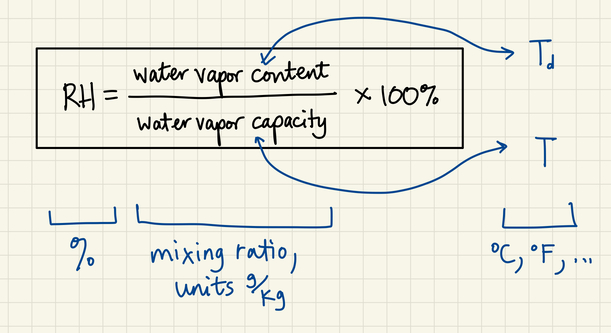
Full RH formula from our notes. To convert between content
and dewpoint, use the chart. To convert between
capacity and temperature, use the same chart again.
And if you are a major, you know this with slightly different symbols:
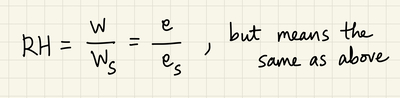
RH formula using either mixing ratio or vapor pressure.
Found this page and not one of my students?
Hi there, welcome! I created this table for my non-major students several years ago (2018 or 2019), and use it in those classes to teach how to calculate relative humidity. I've ignored variations in pressure and may not have used the most accurate form of the Clausius-Clapeyron equation. But if you use it, you should get answers to within ~1-2% and ~1 F of what precise calculators would give you. Feel free to use it for any purpose, just mention where you got it. Thanks for stopping by.